Equilateral triangle
Equilateral triangle
In the familiar Euclidean geometry, equilateral triangles are also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each other and are each 60°. They are regular polygons, and can therefore also be referred to as regular triangles.
Video: What is an equilateral triangle
Principal properties
An equilateral triangle. It has equal sides (a=b=c), equal angles (), and equal altitudes (ha=hb=hc).
Denoting the common length of the sides of the equilateral triangle as a, we can determine using the Pythagorean theorem that:
-
The area is
-
The perimeter is
-
The radius of the circumscribed circle is
-
The radius of the inscribed circle is or
-
The geometric center of the triangle is the center of the circumscribed and inscribed circles
-
And the altitude (height) from any side is .
Denoting the radius of the circumscribed circle as R, we can determine using trigonometry that:
-
The area of the triangle is
Many of these quantities have simple relationships to the altitude ("h") of each vertex from the opposite side:
-
The area is
-
The height of the center from each side, or apothem, is
-
The radius of the circle circumscribing the three vertices is
-
The radius of the inscribed circle is
In an equilateral triangle, the altitudes, the angle bisectors, the ......
‹ Ellipse video up Equilateral triangle video ›

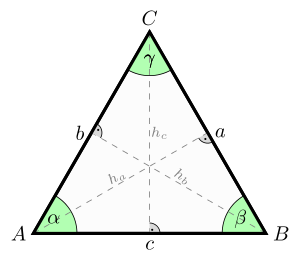
 ), and equal altitudes (ha=hb=hc).
), and equal altitudes (ha=hb=hc).


 or
or 
 .
.





