Proportions
Proportions
What are proportions?
-
If one variable is always the product of the other variable and a constant, the two are said to be directly proportional. x and y are directly proportional if the ratio y/x is constant.
-
If the product of the two variables is always a constant, the two are said to be inversely proportional. x and y are inversely proportional if the product xy is constant.
Direct proportionality
Examples of proportionality
-
If an object travels at a constant speed, then the distance traveled is directly proportional to the time spent traveling, with the speed being the constant of proportionality.
-
The circumference of a circle is directly proportional to its diameter, with the constant of proportionality equal to π.
-
On a map of a sufficiently small area, drawn to scale distances, the distance between any two points on the map is directly proportional to the length of the projected line between the two locations that the points represent, with the constant of proportionality being the scale of the map.
-
The force, acting on a certain object across short distances due to gravity, is directly proportional to the object's sufficiently small mass; the constant of proportionality between the force and the mass is known as gravitational acceleration.
-
The net force acting on an object is proportional to the acceleration of that object. The constant of proportionality in this, Newton's Second Law, is the classical mass of the object.
What are the properties of proportionality?
Inverse proportionality
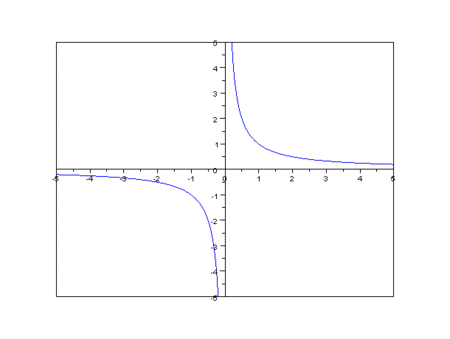
How to calculate inverse proportionality?
Setting up proportions to solve word problems
Solving a proportion with an unknown variable
Let's Review
-
If one variable is always the product of the other variable and a constant, the two are said to be ____ proportional. x and y are ____ proportional if the ratio y/x is constant.
-
If the product of the two variables is always a constant, the two are said to be ____ proportional. x and y are ____ proportional if the product xy is constant.
-
The graph of two variables varying inversely on the Cartesian coordinate plane is a ____ ____ . The product of the x and y values of each point on the curve equals the ____ of ____ (k). Since neither x nor y can equal zero (because k is non-zero), the graph ____ ____ either axis.
Answer
-
If one variable is always the product of the other variable and a constant, the two are said to be directly proportional. x and y are directly proportional if the ratio y/x is constant.
-
If the product of the two variables is always a constant, the two are said to be inversely proportional. x and y are inversely proportional if the product xy is constant.
-
The graph of two variables varying inversely on the Cartesian coordinate plane is a rectangular hyperbola. The product of the x and y values of each point on the curve equals the constant of proportionality (k). Since neither x nor y can equal zero (because k is non-zero), the graph never crosses either axis.
Test Your Knowledge
- Log in or register to post comments
- Email this page







 Hence the constant is the product of x and y.
Hence the constant is the product of x and y.
